-
 support@minemaxx.com
support@minemaxx.com
-
 0086-311-87833311
0086-311-87833311
 NO.8 JIHENG STREET,QIAOXI DISTRICT,SHIJIAZHUANG,HEBEI,CHINA
NO.8 JIHENG STREET,QIAOXI DISTRICT,SHIJIAZHUANG,HEBEI,CHINA
2 月 . 12, 2025 15:05
Back to list
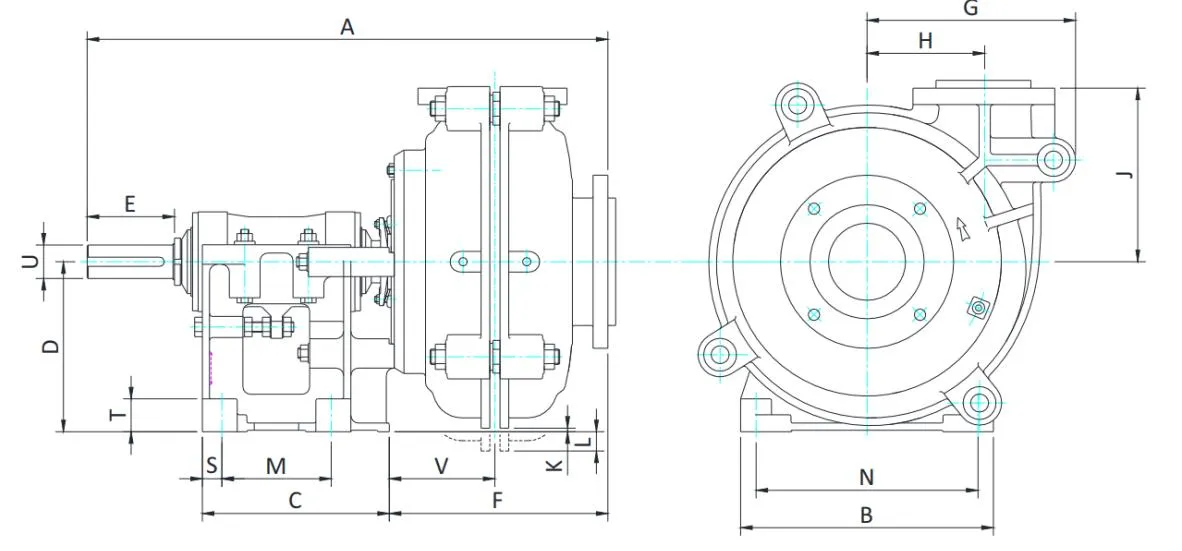
Horizontal Slurry Pumps MM4/3D-AH
Understanding the intricacies of flexible impeller pumps is essential for industry professionals who seek reliable solutions in fluid handling systems. A flexible impeller pump represents a pivotal innovation in engineering, offering unique features and advantages across varied applications.
In addition, flexible impeller pumps offer reversible operation, allowing them to be used for loading and unloading applications without any mechanical alterations. This reversibility is crucial in maritime applications, where ballast and fuel management require efficient and adaptable systems. The ability to pump in both directions enhances versatility, optimizes space, and reduces the need for additional equipment, ultimately saving costs and improving logistics. Energy efficiency is a notable environmental benefit of flexible impeller pumps. The high volumetric efficiency, attributed to the pump's robust design, ensures minimal energy waste during operation. This not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with sustainable practices, advocating for reduced carbon footprints across industries where these pumps are deployed. While the advantages of flexible impeller pumps are numerous, selecting the right model for a specific application requires expert insight. Factors such as fluid viscosity, temperature, desired flow rate, and chemical compatibility must be considered to ensure optimal performance. Engaging with manufacturers who provide detailed consultations and tailored solutions is recommended to maximize the pump's utility and lifespan. In summary, the flexible impeller pump stands out as a versatile, reliable, and efficient component within fluid handling systems. Its self-priming capability, gentle fluid handling, ease of maintenance, reversible operation, and energy efficiency make it a formidable asset across various industries. As technology evolves, these pumps will likely see further enhancements, continuing to uphold their status as a critical element in industrial processes. Trusting in their capabilities is warranted, provided that industry professionals collaborate closely with expert manufacturers to align pump features with specific operational requirements.

In addition, flexible impeller pumps offer reversible operation, allowing them to be used for loading and unloading applications without any mechanical alterations. This reversibility is crucial in maritime applications, where ballast and fuel management require efficient and adaptable systems. The ability to pump in both directions enhances versatility, optimizes space, and reduces the need for additional equipment, ultimately saving costs and improving logistics. Energy efficiency is a notable environmental benefit of flexible impeller pumps. The high volumetric efficiency, attributed to the pump's robust design, ensures minimal energy waste during operation. This not only reduces operational costs but also aligns with sustainable practices, advocating for reduced carbon footprints across industries where these pumps are deployed. While the advantages of flexible impeller pumps are numerous, selecting the right model for a specific application requires expert insight. Factors such as fluid viscosity, temperature, desired flow rate, and chemical compatibility must be considered to ensure optimal performance. Engaging with manufacturers who provide detailed consultations and tailored solutions is recommended to maximize the pump's utility and lifespan. In summary, the flexible impeller pump stands out as a versatile, reliable, and efficient component within fluid handling systems. Its self-priming capability, gentle fluid handling, ease of maintenance, reversible operation, and energy efficiency make it a formidable asset across various industries. As technology evolves, these pumps will likely see further enhancements, continuing to uphold their status as a critical element in industrial processes. Trusting in their capabilities is warranted, provided that industry professionals collaborate closely with expert manufacturers to align pump features with specific operational requirements.
Previous:
Latest news
-
Wet Parts for Optimal PerformanceNewsOct.10,2024
-
Vertical Pump Centrifugal SolutionsNewsOct.10,2024
-
Top Slurry Pump ManufacturersNewsOct.10,2024
-
The Ultimate Guide to Centrifugal Pump for SlurryNewsOct.10,2024
-
Pump Bearing Types for Optimal PerformanceNewsOct.10,2024
-
A Guide to Top Slurry Pump SuppliersNewsOct.10,2024
-
Slurry Pump Parts for Optimal PerformanceNewsSep.25,2024

